
>Publikace>Iowa Gambling Task: Comparison of the Classical Scoring and Cognitive Modeling Approach and its ...
Iowa Gambling Task Scoring Leaders
| CÍGLER, Hynek, Martin ŠMÍRA a Vojtěch VIKTORIN. Iowa Gambling Task: Comparison of the Classical Scoring and Cognitive Modeling Approach and its Convergent Validity with Other Clinical Tasks. In 14th European Conference on Psychological Assessment. 2017. |
| Další formáty: BibTeXLaTeXRIS |
| Základní údaje |
|---|
| Originální název | Iowa Gambling Task: Comparison of the Classical Scoring and Cognitive Modeling Approach and its Convergent Validity with Other Clinical Tasks |
| Název anglicky | Iowa Gambling Task: Comparison of the Classical Scoring and Cognitive Modeling Approach and its Convergent Validity with Other Clinical Tasks |
| Autoři | CÍGLER, Hynek, Martin ŠMÍRA a Vojtěch VIKTORIN. |
| Vydání | 14th European Conference on Psychological Assessment, 2017. |
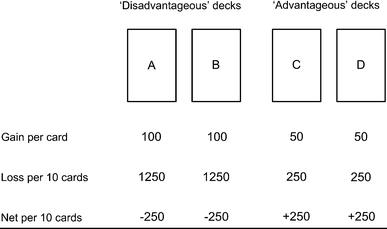
- Studies using the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), a card game that evaluates decision-making by simulating gains and losses in a situation of uncertainty (punishment/reward) reveal that patients who are depressed and/or apathetic show greater impulsiveness and are less effective in performing the tasks (Bechara et al., 2005; Bollon & Bagneux, 2013.
- Iowa Gambling Task, Version 2 igt-2. Length: 15-20 minutes to administer and score. Scoring: Computer Scored. User Level A, M Details Prices. Continue Browsing.
- The Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) is a sequential learning task in which participants develop a tendency towards advantageous options arising from the outcomes associated with their previous decisions. The role of working memory in this complex task has been largely debated in the literature. On one hand, low working memory resources lead to a decrease in the number of advantageous decisions.
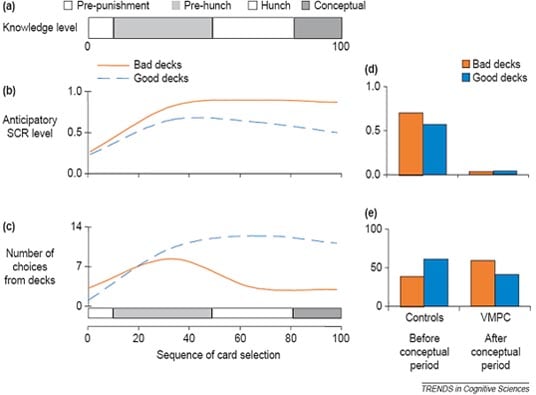
Iowa Gambling Task. The Iowa gambling task is a decision-making task that has been used in an fMRI study of binge drinkers and showed that heavy alcohol users make more disadvantageous decisions on the task than nonusers (Xiao et al., 2013). From: Progress in Brain Research, 2016. Related terms: Impulsivity; Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex.
| Další údaje |
|---|
| Originální jazyk | čeština |
| Typ výsledku | Prezentace na konferencích |
| Obor | 50100 5.1 Psychology and cognitive sciences |
| Stát vydavatele | Česká republika |
| Utajení | není předmětem státního či obchodního tajemství |
| WWW | URL |
| Organizační jednotka | Fakulta sociálních studií |
| Klíčová slova anglicky | Iowa Gambling Task; Cognitive modeling |
| Příznaky | Mezinárodní význam, Recenzováno |
| Změnil | Změnil: Mgr. Martin Šmíra, učo 251591. Změněno: 3. 12. 2017 17:04. |
| Anotace |
|---|
| The aim of this study is to compare Bayesian cognitive modeling of the response style in the Iowa gambling task (IGT), specifically PLV-Delta model (Ahn et al., 2008), and the classical approaches to the IGT scoring in a non-clinical population. We used an exploratory design to analyze convergent validity between different types of the IGT scoring and other clinical tasks in a sample aged 18–30 years. Test battery included Iowa gambling task, SST (stop signal task), go/no-go task, N-back, and DDT (delay discounting task). All these tests were computer-administered. Sample size ranged between 100 and 200 for each pair-wise comparison. Results showed convergent validity between some of the parameters of the cognitive model and the classical IGT test scores; however, the cognitive model parameters show a better incremental validity compared to the traditional scoring techniques. We also estimated reliability of the IGT using several approaches. These results are discussed bearing in mind the exploratory nature of the study. Using point estimate of the parameters from the Bayesian model could limit results of this study. In addition, our reliability estimates are slightly biased due to non-normality of the distribution of all parameters. This study can provide us with a better understanding of the cognitive processes that underlie decision-making in the IGT in a non-clinical population. Moreover, we revealed some advantages of the Bayesian cognitive modeling approach over the classical the IGT scoring. These findings have the potential to improve applicability of the Iowa gambling task in clinical practice. |
| Anotace anglicky |
|---|
| The aim of this study is to compare Bayesian cognitive modeling of the response style in the Iowa gambling task (IGT), specifically PLV-Delta model (Ahn et al., 2008), and the classical approaches to the IGT scoring in a non-clinical population. We used an exploratory design to analyze convergent validity between different types of the IGT scoring and other clinical tasks in a sample aged 18–30 years. Test battery included Iowa gambling task, SST (stop signal task), go/no-go task, N-back, and DDT (delay discounting task). All these tests were computer-administered. Sample size ranged between 100 and 200 for each pair-wise comparison. Results showed convergent validity between some of the parameters of the cognitive model and the classical IGT test scores; however, the cognitive model parameters show a better incremental validity compared to the traditional scoring techniques. We also estimated reliability of the IGT using several approaches. These results are discussed bearing in mind the exploratory nature of the study. Using point estimate of the parameters from the Bayesian model could limit results of this study. In addition, our reliability estimates are slightly biased due to non-normality of the distribution of all parameters. This study can provide us with a better understanding of the cognitive processes that underlie decision-making in the IGT in a non-clinical population. Moreover, we revealed some advantages of the Bayesian cognitive modeling approach over the classical the IGT scoring. These findings have the potential to improve applicability of the Iowa gambling task in clinical practice. |
| Návaznosti |
|---|
| GA15-20970S, projekt VaV | Název: Od rozhodnosti po autoritářství: Potřeba kognitivního uzavření (Akronym: ORAKUZ) |
|---|
| Investor: Grantová agentura ČR, Standardní projekty |
| Typ | Název | Vložil/a | Vloženo |
|---|
| ECPA_v09.pdf | Cígler, H. | 11. 7. 2017 |
Vlastnosti- Adresa v ISu
- https://is.muni.cz/auth/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf
- Adresa ze světa
- https://is.muni.cz/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf
- Adresa do Správce
- https://is.muni.cz/auth/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf?info
- Ze světa do Správce
- https://is.muni.cz/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf?info
- Vloženo
- Út 11. 7. 2017 17:13, Mgr. Hynek Cígler, Ph.D.
Práva- Právo číst
- Právo vkládat
- Právo spravovat
- osoba Mgr. Hynek Cígler, Ph.D., učo 175803
- osoba Mgr. Martin Šmíra, učo 251591
- osoba Mgr. Vojtěch Viktorin, učo 397955
- Atributy
ECPA_v09.pdf- Aplikace
- Otevřít soubor.
Stáhnout soubor. - Adresa v ISu
- https://is.muni.cz/auth/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf
- Adresa ze světa
- http://is.muni.cz/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.pdf
- Typ souboru
- PDF (application/pdf)
- Velikost
- 564,7 KB
- Hash md5
- c909b873cdf7f826d3a698f432649cb0
- Vloženo
- Út 11. 7. 2017 17:13
ECPA_v09.txt- Aplikace
- Otevřít soubor.
Stáhnout soubor. - Adresa v ISu
- https://is.muni.cz/auth/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.txt
- Adresa ze světa
- http://is.muni.cz/publication/1385120/ECPA_v09.txt
- Typ souboru
- holý text (text/plain)
- Velikost
- 13,9 KB
- Hash md5
- 4552f1c883604998311b237a0f19ca87
- Vloženo
- Út 11. 7. 2017 17:20
|
VytisknoutNahlásit neoprávněně vložený soubor
 Zobrazeno: 19. 12. 2020 07:56
Zobrazeno: 19. 12. 2020 07:56



 Zobrazeno: 19. 12. 2020 07:56
Zobrazeno: 19. 12. 2020 07:56